Far upstream element-binding protein 1
| FUBP1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | FUBP1, FBP, FUBP, hDH V, far upstream element binding protein 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 603444; MGI: 1196294; HomoloGene: 48253; GeneCards: FUBP1; OMA:FUBP1 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Far upstream element-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FUBP1 gene.[5][6]
This gene encodes a ssDNA binding protein that activates the far upstream element (FUSE) of c-myc and stimulates expression of c-myc in undifferentiated cells. Regulation of FUSE by FUBP occurs through single-strand binding of FUBP to the non-coding strand. This protein has been shown to function as an ATP-dependent DNA helicase.[6]
Interactions
Far upstream element-binding protein 1 has been shown to interact with MAPK14[7] and SMN1.[8]
Clinical Significance
FUBP1 gene deletion forms part of the 1p/19q codeletion mutation seen in oligodendroglioma, a form of primary brain tumour.[9] CIC gene is also lost in the 1p/19q codeletion mutation.
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000162613 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028034 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Duncan R, Bazar L, Michelotti G, Tomonaga T, Krutzsch H, Avigan M, Levens D (April 1994). "A sequence-specific, single-strand binding protein activates the far upstream element of c-myc and defines a new DNA-binding motif". Genes Dev. 8 (4): 465–80. doi:10.1101/gad.8.4.465. PMID 8125259.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: FUBP1 far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1".
- ^ Kim, Min Jung; Park Bum-Joon; Kang Young-Sun; Kim Hyoung June; Park Jae-Hyun; Kang Jung Woo; Lee Sang Won; Han Jung Min; Lee Han-Woong; Kim Sunghoon (July 2003). "Downregulation of FUSE-binding protein and c-myc by tRNA synthetase cofactor p38 is required for lung cell differentiation". Nat. Genet. 34 (3). United States: 330–6. doi:10.1038/ng1182. ISSN 1061-4036. PMID 12819782. S2CID 41006480.
- ^ Williams, B Y; Hamilton S L; Sarkar H K (March 2000). "The survival motor neuron protein interacts with the transactivator FUSE binding protein from human fetal brain". FEBS Lett. 470 (2). NETHERLANDS: 207–10. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01320-X. ISSN 0014-5793. PMID 10734235. S2CID 28330997.
- ^ Weller, Michael (8 December 2020). "EANO guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diffuse gliomas of adulthood". Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology. 18 (3): 170–186. doi:10.1038/s41571-020-00447-z. PMC 7904519. PMID 33293629.
Further reading
- Williams BY, Hamilton SL, Sarkar HK (2000). "The survival motor neuron protein interacts with the transactivator FUSE binding protein from human fetal brain". FEBS Lett. 470 (2): 207–10. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01320-X. PMID 10734235. S2CID 28330997.
- Liu J, He L, Collins I, et al. (2000). "The FBP interacting repressor targets TFIIH to inhibit activated transcription". Mol. Cell. 5 (2): 331–41. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80428-1. PMID 10882074.
- Markovtsov V, Nikolic JM, Goldman JA, et al. (2000). "Cooperative assembly of an hnRNP complex induced by a tissue-specific homolog of polypyrimidine tract binding protein". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (20): 7463–79. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.20.7463-7479.2000. PMC 86300. PMID 11003644.
- He L, Weber A, Levens D (2000). "Nuclear targeting determinants of the far upstream element binding protein, a c-myc transcription factor". Nucleic Acids Res. 28 (22): 4558–65. doi:10.1093/nar/28.22.4558. PMC 113884. PMID 11071946.
- Vindigni A, Ochem A, Triolo G, Falaschi A (2001). "Identification of human DNA helicase V with the far upstream element-binding protein". Nucleic Acids Res. 29 (5): 1061–7. doi:10.1093/nar/29.5.1061. PMC 29729. PMID 11222755.
- Liu J, Akoulitchev S, Weber A, et al. (2001). "Defective interplay of activators and repressors with TFIH in xeroderma pigmentosum". Cell. 104 (3): 353–63. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00223-9. PMID 11239393.
- Braddock DT, Louis JM, Baber JL, et al. (2002). "Structure and dynamics of KH domains from FBP bound to single-stranded DNA". Nature. 415 (6875): 1051–6. Bibcode:2002Natur.415.1051B. doi:10.1038/4151051a. PMID 11875576. S2CID 4401103.
- Rappsilber J, Ryder U, Lamond AI, Mann M (2002). "Large-scale proteomic analysis of the human spliceosome". Genome Res. 12 (8): 1231–45. doi:10.1101/gr.473902. PMC 186633. PMID 12176931.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Kim MJ, Park BJ, Kang YS, et al. (2003). "Downregulation of FUSE-binding protein and c-myc by tRNA synthetase cofactor p38 is required for lung cell differentiation". Nat. Genet. 34 (3): 330–6. doi:10.1038/ng1182. PMID 12819782. S2CID 41006480.
- Brandenberger R, Wei H, Zhang S, et al. (2005). "Transcriptome characterization elucidates signaling networks that control human ES cell growth and differentiation". Nat. Biotechnol. 22 (6): 707–16. doi:10.1038/nbt971. PMID 15146197. S2CID 27764390.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112130B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Kouzine F, Liu J, Sanford S, et al. (2004). "The dynamic response of upstream DNA to transcription-generated torsional stress". Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11 (11): 1092–100. doi:10.1038/nsmb848. PMID 15502847. S2CID 28956216.
- Rush J, Moritz A, Lee KA, et al. (2005). "Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells". Nat. Biotechnol. 23 (1): 94–101. doi:10.1038/nbt1046. PMID 15592455. S2CID 7200157.
- Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, et al. (2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0010-8592-0. PMID 16169070.
- Fautsch MP, Vrabel AM, Johnson DH (2006). "The identification of myocilin-associated proteins in the human trabecular meshwork". Exp. Eye Res. 82 (6): 1046–52. doi:10.1016/j.exer.2005.09.016. PMID 16289162.
- Liu J, Kouzine F, Nie Z, et al. (2006). "The FUSE/FBP/FIR/TFIIH system is a molecular machine programming a pulse of c-myc expression". EMBO J. 25 (10): 2119–30. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601101. PMC 1462968. PMID 16628215.
- Ko HS, Kim SW, Sriram SR, et al. (2006). "Identification of far upstream element-binding protein-1 as an authentic Parkin substrate". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (24): 16193–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.C600041200. PMID 16672220.
- v
- t
- e
-
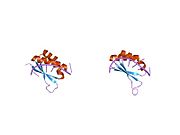 1j4w: COMPLEX OF THE KH3 and KH4 DOMAINS OF FBP WITH A SINGLE_STRANDED 29mer DNA OLIGONUCLEOTIDE FROM THE FUSE ELEMENT OF THE C-MYC ONCOGENE
1j4w: COMPLEX OF THE KH3 and KH4 DOMAINS OF FBP WITH A SINGLE_STRANDED 29mer DNA OLIGONUCLEOTIDE FROM THE FUSE ELEMENT OF THE C-MYC ONCOGENE -
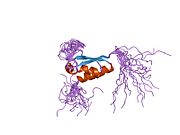 1x4m: Solution structure of KH domain in Far upstream element binding protein 1
1x4m: Solution structure of KH domain in Far upstream element binding protein 1 -
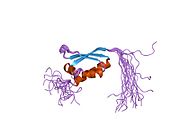 1x4n: Solution structure of KH domain in FUSE binding protein 1
1x4n: Solution structure of KH domain in FUSE binding protein 1
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 1 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e





















