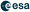Hakuto-R Mission 2
 Full-size model of Hakuto-R | |
| Mission type | Technology demonstration |
|---|---|
| Operator | ispace |
| Website | ispace-inc |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Hakuto-R M2 |
| Spacecraft type | Lunar lander |
| Manufacturer | ispace |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | December 2024 (planned) |
| Rocket | Falcon 9 Block 5 |
| Contractor | SpaceX |
← Hakuto-R Mission 1 Hakuto-R Mission 3 → | |
Hakuto-R Mission 2 is a robotic lunar landing mission planned for December 2024.[1] Developed by ispace, the lander will deliver a new micro rover manufactured by the company, and other payloads. Like Hakuto-R Mission 1 this mission will serve as a technology demonstration, with the final goal of providing reliable transportation and data services on the moon. The lander is named Resilience.[2]
Background
The project began development after the Hakuto-R Mission 1 in 2023. The mission plans to use the same overall design with upgrades from the flight data collected in mission 1.[3]
Lander specifications
The Resilience lander will stand 2.5 by 2.3 meters and has a weight of 340 kg. The lander will include a micro rover that is planned to perform an ISRU demonstration.[4]
Mission
The mission is planned to launch no earlier than December 2024.[5] The lander will also carry a memory disk developed by the UNESCO organization carrying 275 languages and other cultural artifacts.[6] The lander completed successful vacuum testing in June 2024.[7] In August 2024, the rover which will be integrated with the lander was completed.[8]
Landing site

The intended landing site for mission is in Mare Frigoris, a location allowing continuous line-of-sight radio communication from Earth.[5]
Rover
The mission includes a 5 kg (11 lb) rover designed and manufactured in Luxembourg which will explore the area around the landing site, after being lowered to the lunar surface from the lander.[9]
Payloads
In addition to the rover the lander will carry payloads from Takasago Thermal Engineering Co., Euglena Co., National Central University and Bandai Namco Research Institute, Inc.[5]
See also
References
- ^ Foust, Jeff (12 September 2024). "Second ispace lunar lander planned for launch in December". SpaceNews. Retrieved 12 September 2024.
- ^ "ispace Announces Mission 2 with Unveiling of Micro Rover Design". ispace. Retrieved 2024-06-22.
- ^ Dixit, Mrigakshi. "Japan's ispace aims for moon landing in 2024 with upgraded lander". Interesting Engineering. Retrieved 2024-06-22.
- ^ Alamalhodaei, Aria (2023-11-16). "Despite setbacks, ispace to launch second moon mission in Q4 2024". TechCrunch. Retrieved 2024-06-22.
- ^ a b c "ispace Announces Launch Timing, RESILIENCE Lander Progress, and Planned Lunar Landing Zone During Mission 2 Update Press Conference". 2024-09-12.
- ^ Meredith Garofalo (2024-05-08). "Private lunar lander to carry 'memory disk' of 275 human languages to the moon in 2024". Space.com. Retrieved 2024-06-22.
- ^ "ispace RESILIENCE Lunar Lander Successfully Achieves Testing Milestone in Preparation for Mission 2". ispace. Retrieved 2024-06-30.
- ^ NEWS, KYODO. "ispace's lunar rover arrives in Japan to prepare for 2nd space probe". Kyodo News+. Retrieved 2024-09-06.
- ^ "ispace-EUROPE announces Completion of First European Designed, Manufactured, and Assembled Lunar Micro Rover". 2024-07-25.
- v
- t
- e
programs
missions
| Orbiters |
|
|---|---|
| Landers | |
| Rovers | |
| Flybys |
missions
| Crewed landings | |
|---|---|
| Orbiters |
|
| Impactors | |
| Landers | |
| Rovers |
|
| Sample return | |
| Failed landings |
|
| Flybys |
missions
| Artemis |
|
|---|---|
| CLPS |
|
| Luna-Glob | |
| CLEP | |
| Others |
|
missions
| Robotic |
|
|---|---|
| Crewed |
concepts
- Altair
- Baden-Württemberg 1
- #dearMoon project
- European Lunar Explorer
- First Lunar Outpost
- International Lunar Network
- LEO
- LK
- Lunar-A
- Lunar Lander
- Lunar Mission One
- Lunar Observer
- Lunokhod 3
- MoonLITE
- MoonRise
- OrbitBeyond
- Project Harvest Moon
- Prospector
- Resource Prospector
- SELENE-2
- Ukrselena
- XL-1
- VIPER
- Colonization of the Moon
- Google Lunar X Prize
- List of lunar probes
- List of missions to the Moon
- List of artificial objects on the Moon
- List of species that have landed on the Moon
- Lunar resources
- Apollo 17 Moon mice
- Moon landing conspiracy theories
- Third-party evidence for Apollo Moon landings
- Apollo 11 anniversaries
- List of crewed lunar landers
- Missions are ordered by launch date. Crewed missions are in italics.