位相幾何学者の正弦曲線(いそうきかがくしゃのせいげんきょくせん、英: Topologist's sine curve)とは、半開区間 ![{\displaystyle (0,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7e70f9c241f9faa8e9fdda2e8b238e288807d7a4) 上の関数
上の関数  に原点
に原点  を加えた、座標平面上の曲線である。すなわち、位相幾何学者の正弦曲線
を加えた、座標平面上の曲線である。すなわち、位相幾何学者の正弦曲線  は、以下の式で与えられる。
は、以下の式で与えられる。
![{\displaystyle T=\left\{\left(x,\sin {\frac {1}{x}}\right):x\in (0,1]\right\}\cup \{(0,0)\}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c188bad1bd5484857ca8ee5dbd5e1354243bb0f9)
この曲線は、数学、特に位相幾何学において、いくつかの興味深い性質を持つ位相空間の例としてしばしば取り上げられる。
曲線の概形
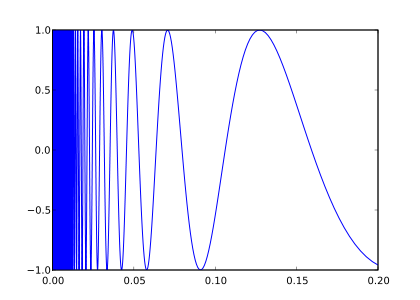
 が右から0に近づくにつれて
が右から0に近づくにつれて  は大きくなり、正弦波の周期は急速に減少していく。
は大きくなり、正弦波の周期は急速に減少していく。
性質
位相幾何学者の正弦曲線  は連結であるが、局所連結でも弧状連結でもない。
は連結であるが、局所連結でも弧状連結でもない。  は原点を含むが、原点と関数のグラフ上の点とを結ぶ弧を作ることはできないからである。
は原点を含むが、原点と関数のグラフ上の点とを結ぶ弧を作ることはできないからである。
位相空間  は局所コンパクト空間の連続像である。実際、
は局所コンパクト空間の連続像である。実際、  を {−1} ∪ (0, 1] とし、
を {−1} ∪ (0, 1] とし、  から
から  への写像
への写像  を
を

と定めればよい。しかし、  自身は局所コンパクトではない。
自身は局所コンパクトではない。
 のルベーグ被覆次元は1である。
のルベーグ被覆次元は1である。
亜種
位相幾何学者の正弦曲線の2つの亜種は、異なる興味深い性質を持つ。
閉じた位相幾何学者の正弦曲線は、位相幾何学者の正弦曲線に集積点の集合 ![{\displaystyle \{(0,y)\mid y\in [-1,1]\}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3dff9ac5c2a53868d76f8bf3f7a7a841876b3ca0) を加えたものとして定義される。この空間は有界閉集合なのでハイネ・ボレルの被覆定理によりコンパクトである。しかし、位相幾何学者の正弦曲線と同様に、連結ではあるが局所連結でも弧状連結でもない。
を加えたものとして定義される。この空間は有界閉集合なのでハイネ・ボレルの被覆定理によりコンパクトである。しかし、位相幾何学者の正弦曲線と同様に、連結ではあるが局所連結でも弧状連結でもない。
拡張された位相幾何学者の正弦曲線は、閉じた位相幾何学者の正弦曲線に集合 ![{\displaystyle \{(x,1)\mid x\in [0,1]\}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5327e8b84efd6909fc334b522974b34963cd7e8f) を加えたものとして定義される。この空間は弧連結ではあるが、局所連結ではない。
を加えたものとして定義される。この空間は弧連結ではあるが、局所連結ではない。
参考文献
- Steen, Lynn Arthur; Seebach, J. Arthur Jr. (1995) [1978], Counterexamples in Topology (Dover reprint of 1978 ed.), Mineola, NY: Dover Publications, Inc., pp. 137?138, ISBN 978-0-486-68735-3, MR1382863
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Topologist's Sine Curve". mathworld.wolfram.com (英語).

![{\displaystyle (0,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7e70f9c241f9faa8e9fdda2e8b238e288807d7a4)



![{\displaystyle T=\left\{\left(x,\sin {\frac {1}{x}}\right):x\in (0,1]\right\}\cup \{(0,0)\}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c188bad1bd5484857ca8ee5dbd5e1354243bb0f9)





![{\displaystyle \{(0,y)\mid y\in [-1,1]\}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3dff9ac5c2a53868d76f8bf3f7a7a841876b3ca0)
![{\displaystyle \{(x,1)\mid x\in [0,1]\}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5327e8b84efd6909fc334b522974b34963cd7e8f)






