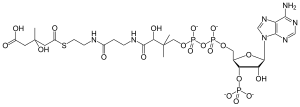
베타-하이드록시 베타-메틸글루타릴-CoA
 | |
| 이름 | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC 이름 (9R,21S)-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]-3,5,9,21-tetrahydroxy-8,8,21-trimethyl-10,14,19-trioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-18-thia-11,15-diaza-3,5-diphosphatricosan-23-oic acid 3,5-dioxide | |
| 식별자 | |
| |
3D 모델 (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.820 |
IUPHAR/BPS |
|
| MeSH | HMG-CoA |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
SMILES
| |
| 성질 | |
| C27H44N7O20P3S | |
| 몰 질량 | 911.661 g/mol |
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하면, 표준상태(25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa)에서 물질의 정보가 제공됨.  예 확인 (관련 정보 예 확인 (관련 정보  예 예 아니오 ?) 아니오 ?) 정보상자 각주 | |
β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA(영어: β-hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA, HMG-CoA) 또는 3-하이드록시 3-메틸글루타릴-CoA(영어: 3-hydroxy 3-methylglutaryl-CoA)는 메발론산 경로 및 케톤체생성 경로의 대사 중간생성물이다. β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA(HMG-CoA)는 β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA 생성효소(HMG-CoA 생성효소)에 의해 아세틸-CoA와 아세토아세틸-CoA로부터 생성된다. 1950년대에 일리노이 대학교 어배너-섐페인의 마이너 제서 쿤(Minor Jesser Coon)과 비말 쿠마르 바크하와트(Bimal Kumar Bachhawat)의 연구가 이러한 발견을 이끌었다.[1][2]
β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA(HMG-CoA)는 류신, 아이소류신, 발린과 같은 가지사슬 아미노산의 대사 과정에서의 대사 중간생성물이다.[3] β-메틸글루타코닐-CoA(MG-CoA)와 β-하이드록시 β-메틸뷰티릴-CoA(HMB-CoA)는 β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA(HMG-CoA)의 직접적인 전구물질들이다.
생합성
 |
메발론산 경로
메발론산의 합성은 두 분자의 아세틸-CoA가 싸이올레이스에 의해 클라이젠 축합되어 아세토아세틸-CoA를 생성하는 것으로 시작된다. 다음 반응은 아세틸-CoA와 아세토아세틸-CoA가 β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA 생성효소(HMG-CoA 생성효소)에 의해 β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA(HMG-CoA)를 생성하는 반응이다.[7]
메발론산 생합성의 마지막 단계는 β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA(HMG-CoA)가 NADPH 의존성 산화환원효소인 β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA 환원효소(HMG-CoA 환원효소)에 의해 메발론산으로 전환되는 것이며, 이 단계는 메발론산 경로의 주요 조절 지점이다. 메발론산은 사람에서 콜레스테롤을 포함한 다양한 최종 산물들을 포괄하는 아이소프레노이드들의 전구물질로 역할을 한다.[8]
 |
케톤체생성 경로
β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA 분해효소(HMG-CoA 분해효소)는 β-하이드록시 β-메틸글루타릴-CoA(HMG-CoA)를 아세틸-CoA와 아세토아세트산으로 분해한다.
 |
같이 보기
- β-메틸글루타코닐-CoA
- 스테로이드생성 효소
각주
- ↑ Sarkar DP (2015). “Classics in Indian Medicine” (PDF). 《The National Medical Journal of India》 (28): 3. 2016년 5월 31일에 원본 문서 (PDF)에서 보존된 문서.
- ↑ Surolia A (1997). “An outstanding scientist and a splendid human being” (PDF). 《Glycobiology》 7 (4): v–ix. doi:10.1093/glycob/7.4.453.
- ↑ “Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation - Reference pathway”. 《Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes》. Kanehisa Laboratories. 2016년 1월 27일. 2018년 2월 1일에 확인함.
- ↑ Wilson JM, Fitschen PJ, Campbell B, Wilson GJ, Zanchi N, Taylor L, Wilborn C, Kalman DS, Stout JR, Hoffman JR, Ziegenfuss TN, Lopez HL, Kreider RB, Smith-Ryan AE, Antonio J (February 2013). “International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB)”. 《Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition》 10 (1): 6. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-10-6. PMC 3568064. PMID 23374455.
- ↑ Zanchi NE, Gerlinger-Romero F, Guimarães-Ferreira L, de Siqueira Filho MA, Felitti V, Lira FS, Seelaender M, Lancha AH (April 2011). “HMB supplementation: clinical and athletic performance-related effects and mechanisms of action”. 《Amino Acids》 40 (4): 1015–1025. doi:10.1007/s00726-010-0678-0. PMID 20607321.
HMB is a metabolite of the amino acid leucine (Van Koverin and Nissen 1992), an essential amino acid. The first step in HMB metabolism is the reversible transamination of leucine to [α-KIC] that occurs mainly extrahepatically (Block and Buse 1990). Following this enzymatic reaction, [α-KIC] may follow one of two pathways. In the first, HMB is produced from [α-KIC] by the cytosolic enzyme KIC dioxygenase (Sabourin and Bieber 1983). The cytosolic dioxygenase has been characterized extensively and differs from the mitochondrial form in that the dioxygenase enzyme is a cytosolic enzyme, whereas the dehydrogenase enzyme is found exclusively in the mitochondrion (Sabourin and Bieber 1981, 1983). Importantly, this route of HMB formation is direct and completely dependent of liver KIC dioxygenase. Following this pathway, HMB in the cytosol is first converted to cytosolic β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), which can then be directed for cholesterol synthesis (Rudney 1957) (Fig. 1). In fact, numerous biochemical studies have shown that HMB is a precursor of cholesterol (Zabin and Bloch 1951; Nissen et al. 2000).
- ↑ Kohlmeier M (May 2015). 〈Leucine〉. 《Nutrient Metabolism: Structures, Functions, and Genes》 2판. Academic Press. 385–388쪽. ISBN 978-0-12-387784-0. 2016년 6월 6일에 확인함.
Energy fuel: Eventually, most Leu is broken down, providing about 6.0kcal/g. About 60% of ingested Leu is oxidized within a few hours ... Ketogenesis: A significant proportion (40% of an ingested dose) is converted into acetyl-CoA and thereby contributes to the synthesis of ketones, steroids, fatty acids, and other compounds
Figure 8.57: Metabolism of L-leucine - ↑ Garrett RH (2013). 《Biochemistry》. Cengage Learning. 856쪽. ISBN 978-1-305-57720-6.
- ↑ Haines BE, Steussy CN, Stauffacher CV, Wiest O (October 2012). “Molecular modeling of the reaction pathway and hydride transfer reactions of HMG-CoA reductase”. 《Biochemistry》 51 (40): 7983–95. doi:10.1021/bi3008593. PMC 3522576. PMID 22971202.
- v
- t
- e
| HMG-CoA로 |
|
|---|---|
| 케톤체 | |
| DMAPP로 |
|
| 제라닐- | |
| 카로티노이드 |
|
(스테롤으로)
- 22R-하이드록시콜레스테롤
- 20α,22R-다이하이드록시콜레스테롤
| 피토스테롤 | |
|---|---|
| 에르고스테롤 |
- 생체분자: 탄수화물
- 당단백질
- 글리코사이드
- 지질
- 지방산 / 지방산 대사 중간생성물
- 인지질
- 스핑고지질
- 스테로이드
- 에이코사노이드
- 단백질
- 단백질생성성 아미노산 / 아미노산 대사 중간생성물
- 핵산
- 구성 성분
- 뉴클레오타이드 대사 중간생성물
- 테트라피롤
- 헴 대사 중간생성물
- 알코올







